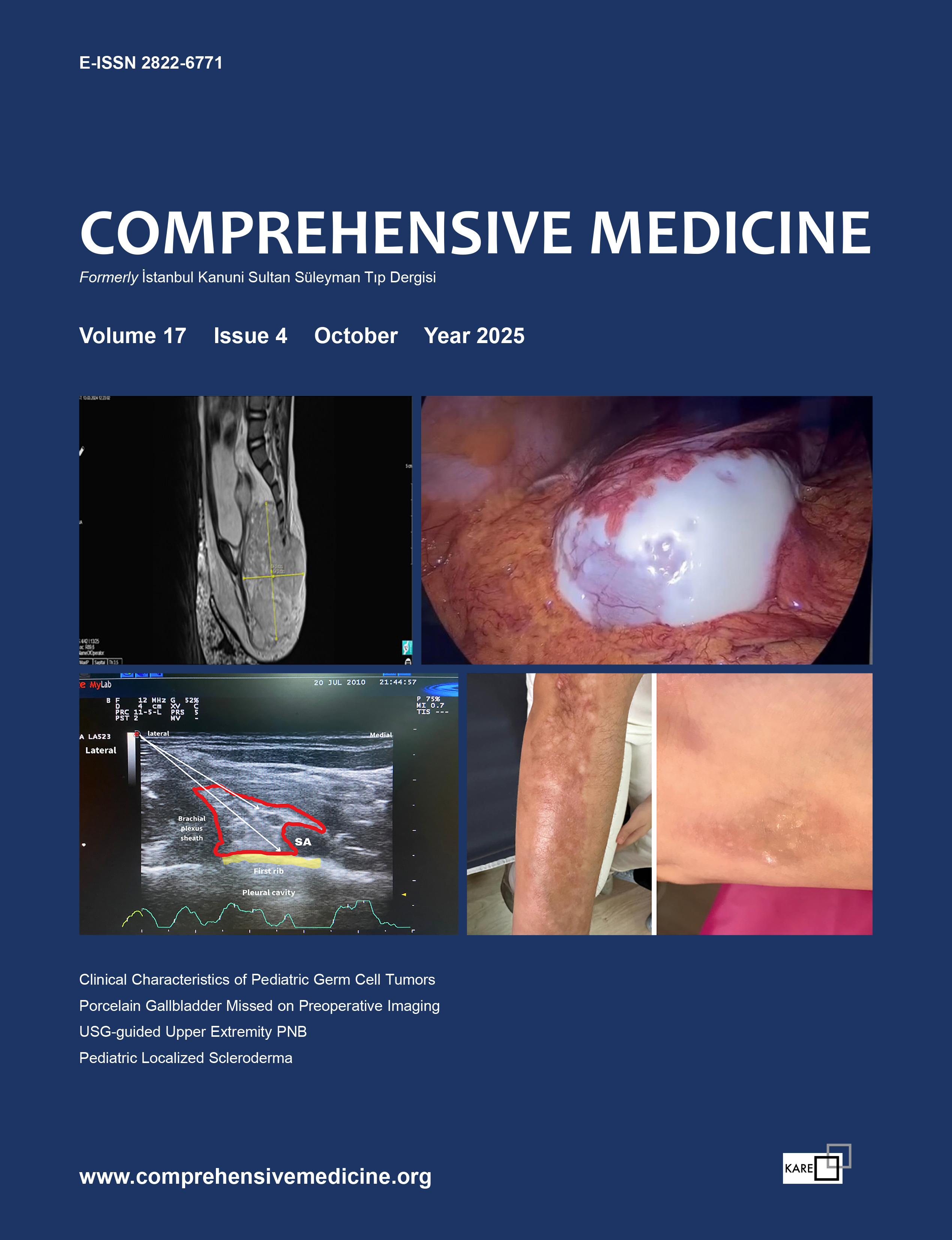
Terminated congenital vertebral abnormalities during 2002 and 2007
Ali Gedikbaşı1, Gökhan Yıldırım1, Emel Asar Canaz1, Gülseren Aslan2, M. Akif Sargın1, Sibel Özbek3, Sultan Kavuncuoğlu3, Yavuz Ceylan11Bakirkoy Woman And Child Education And Research Hospital Gynecology And Obstetric Clinic2Bakırköy Woman And Child Education And Research Hospital Pediatric Neurology Unit
3Bakırköy Woman And Child Education And Research Hospital Neonatology Unit
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the dispersion of congenital vertebra abnormalities detected and terminated in our perinatology department.
METHODS: One hundred and seventy one cases with congenital vertebra anomalies, which were evaluated in the hospital’s neonatology-perinatology council and decision of parents for pregnancy termination were analyzed retrospectively.
RESULTS: Among 171 patients with vertebra abnormalities, 153 cases with open neural tube defects were found. Spina bifida was most commonly associated with anencephaly (31.2 %) and acrania (9.7 %), followed by iniencephaly (7.6 %). In cases with intracranial pathologic development, termination of pregnancy was recommended. Six cases with iniencephaly were observed and terminated. Of seven cases with scoliosis, 3 cases were associated with open neural tube defect and the other 4 were complicated with skeletal dysplasia. Two cases with hemivertebra decided for termination of pregnancy. One case with diastematomyelia were associated with neural tube defect. We found also one case with caudal regression, another one with sirenomelia with decision for termination. In 4 of 5 cases with sacrococcygeal teratoma, hydrops developed following intrauterine fetal demise.
CONCLUSION: Vertebral malformations develop in early embryogenesis and early prenatal diagnosis is possible. However, the prognosis of vertebral pathologies deteriorate with intracranial interaction. The option of pregnancy termination should be offered to this group.
Keywords: prenatal diagnosis, spina bifida, iniencephaly, scoliosis, hemivertebra, diastematomyelia, sacral agenesis, sirenomelia, sacrococcygeal teratoma
2002 ile 2007 yılları arasında sonlandırılan doğumsal vertebra anomalileri
Ali Gedikbaşı1, Gökhan Yıldırım1, Emel Asar Canaz1, Gülseren Aslan2, M. Akif Sargın1, Sibel Özbek3, Sultan Kavuncuoğlu3, Yavuz Ceylan11Sb Bakırköy Kadın Ve Çocuk Hast. Eğitim Ve Araşt. Hastanesi Kadın Hast. Ve Doğum Kliniği2Sb Bakırköy Kadın Doğum Ve Çocuk Hast. Eğt. Arş. Hastanesi Çocuk Nörolojisi Bölümü
3Sb Bakırköy Kadın Doğum Ve Çocuk Hast. Eğt. Arş. Hastanesi Çocuk Yenidoğan Bölümü
AMAÇ: Perinatoloji ünitesinde saptanan ve gebelik sonlandırmasına giden konjenital vertebra anomalilerin dağılımı.
YÖNTEMLER: 2002-2007 yılları arasında hastanemiz yenidoğan-perinatoloji konseyinde görüşülen, danışma aldıktan sonra sonlandırmayı seçen 171 doğumsal vertebra patolojisi retrospektif olarak incelenmiştir.
BULGULAR: Vertebra anomalisi olan 171 olgunun 153’ü nde açık nöral tüp defekti bulunmuştur. Spina bifida bulgularına eşlik eden en sık anomaliler anensefali (% 31.2), akrani (% 9.7) ve iniensefali (% 7.6) olmuştur. Intrakranial yapılarda patolojik gelişim saptanan olgulara gebelik sonlandırması önerilmiştir. Altı izole iniensefali olgusu saptanmış ve sonlandırılmıştır. Yedi skolyoz olgusunun 3 tanesi açık nöral tüp defektleri ile birlikte olup, diğer 4 skolyoz hepsinde eşlik eden iskelet displazileri görülmüştür. İki hemivertebra olgusunda ebeveynler gebeliği sonlandırmaya karar vermiştir. Bir diastematomiyelia olgusunun nöral tüp defektine eşlik ettiği görülmüştür. Aynı şekilde bir kaudal regresyon sendromu ve bir sirenomelia olgusu gebeliği sonlandırmıştır. Beş tane sakrokoksigeal teratom olgusunun dört tanesinde hydrops gelişmiş ve intrauterine fetal kayıp gerçekleşmiştir.
SONUÇ: Vertebra anomaliler embriyogenezin erken dönemlerinde gelişir ve erken tanısı olasıdır. Bununla birlikte, vertebra anomalilerde prognoz, intrakraniyal etkileşim nedeniyle olumsuzlaşmaktadır. Bu hastalara gebelik sonlandırması seçeneği sunulabilmelidir.
Anahtar Kelimeler: prenatal tanı, spina bifida, iniensefali, skolyoz, hemivertebra, diastematomiyelia, sakral agenezi, sirenomelia, sakrokosigeal teratom
Manuscript Language: Turkish