Quick Search
Volume: 17 Issue: 1 - 2025
| 1. | Front Matter Pages I - V |
| RESEARCH ARTICLE | |
| 2. | The Effect of Novel Inflammatory Biomarkers on Determining Early Mortality After Cardiac Surgery in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure Bedih Balkan, Barış Timur doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.40427 Pages 1 - 7 INTRODUCTION: Various hemogram parameters have been used for predicting mortality in intensive care. In this study, the effect of new inflammatory biomarkers such as mean platelet volume, platelet/lymphocyte ratio, and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio on early mortality was researched in patients with chronic renal failure, who had a cardiac surgery operation. METHODS: All the patients with preoperative chronic renal failure who underwent on-pump or off-pump cardiac surgery in our clinic between September 2016-September 2019 were examined. Patients’ demographic data, preoperative hemoglobin, platelet/lymphocyte, neutrophil/lymphocyte, and mean platelet volume and postoperative hemoglobin, platelet/lymphocyte, neutrophil/lymphocyte and MPV were reviewed. Whether there is a difference in on-pump and off-pump surgeries on the matter and their 30-day surgical mortality were assessed in intensive care follow-ups. RESULTS: Of the patients included in the study within the preoperative period, 74 (60%) had DM and 94 (76.4%) were hypertensive. The mean duration of the patients’ hospitalization was found as 13.88±2.4 days. Thirty-day surgical mortality: 30 (24.4%); preoperative and postoperative, platelet/lymphocyte, neutrophil/lymphocyte of the patients did not appear significant. It was found that MPV in the on-pump group was significantly higher in both preoperative and postoperative values than in the off-pump group. Preoperative PLR and NLR values were significantly lower (p<0.05) in the off-pump group. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: MPV is an important marker in determining the postoperative mortality in patients with chronic renal failure who had cardiac surgery. |
| 3. | Evaluation of Ocular Anterior Segment Parameters in Vitiligo Patients with Periocular Involvement Delil Özcan, Hazel Kaya doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.28190 Pages 8 - 12 INTRODUCTION: This study aimed to quantitatively evaluate changes in the corneal and lenticular structures in vitiligo patients with periocular involvement. METHODS: Thirty patients with vitiligo and periocular involvement, along with 30 healthy volunteers, were included in the study. The anterior segment parameters were evaluated using specular microscopy and corneal topography. To evaluate the corneal endothelium, the mean cell area, mean endothelial cell density, coefficient of variation in the cell area, and central corneal thickness (CCT) were measured using specular microscopy. The mean anterior chamber depth (ACD), mean anterior chamber angle (ACA), mean keratometry (Km), and lens densitometry values were measured using corneal topography, and all parameters were compared between the groups. RESULTS: There were no statistically significant differences in endothelial parameters, CCT, ACD, ACA, and Km values between the vitiligo patients and the control group (p>0.05). Additionally, there was no statistically significant difference in lens densitometry values in any zone between patients with vitiligo and the control group (p>0.05). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that anterior segment parameters are not affected in patients with periocular vitiligo, and the pathological destruction seen in melanocytes in vitiligo is not observed in the neural crest-derived cells of the cornea. |
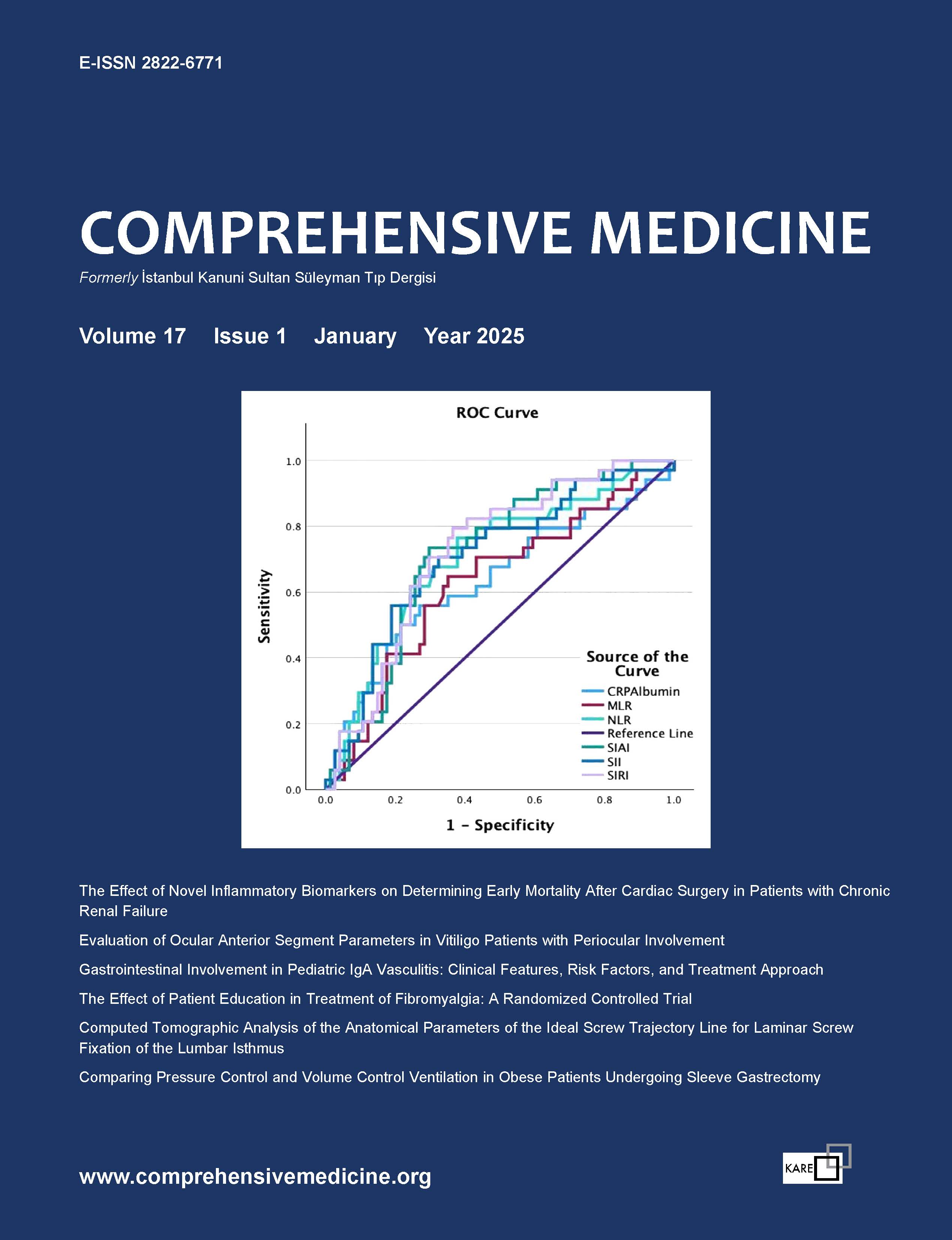
| 4. | Gastrointestinal Involvement in Pediatric IgA Vasculitis: Clinical Features, Risk Factors, and Treatment Approach Şengül Çağlayan, Sümeyra Başaran Çoban, Kadir Ulu, Betül Sözeri doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.09609 Pages 13 - 21 INTRODUCTION: This study aimed to evaluate the clinical and laboratory characteristics of gastrointestinal (GI) involvement in pediatric IgA vasculitis (IgAV) patients, with a particular focus on identifying risk factors for severe complications and exploring current management strategies. METHODS: This retrospective cohort study included pediatric patients diagnosed with IgAV who were followed at a tertiary medical center between January 2019 and March 2024. Patients were divided into two groups—severe and non-severe GI involvement—and data were analyzed comparatively. RESULTS: A total of 265 patients were included in the study, of whom 109 (41.1%) had GI involvement. Among these, 35 (32.1%) were classified as having severe GI involvement, while 74 (67.9%) were categorized as having non-severe involvement. All patients with GI symptoms reported abdominal pain, with 37 (33.9%) experiencing nausea and vomiting. Positive fecal occult blood tests were observed in 59 (54.1%) patients, melena in 4 (3.6%), and hematochezia in 14 (12.8%). Radiological findings showed intestinal wall edema in 28 (25.6%) patients, intussusception in 7 (6.4%), and intestinal perforation in 1 patient (0.9%). Laboratory markers such as NLR, MLR, SII, SIRI, SIAI, and CRP/albumin ratios were significantly elevated in the severe GI involvement group (p<0.05), while albumin levels were significantly lower (p<0.001). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: NLR, MLR, SII, SIRI, SIAI, and CRP/albumin ratios were found to predict severe GI involvement, demonstrating their potential as useful clinical tools for early identification of high-risk patients. |
| 5. | The Effect of Patient Education in Treatment of Fibromyalgia: A Randomized Controlled Trial Hatice Kübra Aşık, Saliha Eroğlu Demir, Nihal Özaras, Aylin Rezvani, Teoman Aydın, Mustafa Güler, Sevde Poşul, Emine Poyraz doi: 10.14744/cm.2025.30085 Pages 22 - 28 INTRODUCTION: Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) can be treated with a variety of pharmaceutical and non-pharmacological approaches. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of patient education and a home exercise program on FMS patients' pain, fatigue, functioning, and quality of life METHODS: The study included patients who satisfied the American College of Rheumatology's FMS criteria. They were split up into two groups at random. A schedule of at-home exercise was given to both groups. Furthermore, Group 2 patients participated in patient education sessions. At baseline and eight weeks later, both groups underwent examinations. Evaluation criteria included the Nottingham Health Profile (NHP) for quality of life, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) for psychological status, the Visual Analogue Scale for pain severity (VASp) and exhaustion (VASf), and the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ) for functional status. RESULTS: The primary clinical and demographic characteristics of the two groups were comparable at baseline. Although the values of VASp (p=0.014), VASf (p=0.011), BDI (p=0.043), NHP subscales (p<0.05), FIQ (p=0.012) showed statistically significant improvements in Group 2, only Group 1's FIQ score significantly improved (p=0.027). There were substantial differences in VASp (p=0.026), VASf (p<0.001), BDI (p<0.001), and all NHP subscales except sleep problems, FIQ scores (p=0.036) between the two groups in favor of Group 2 at the end of eight weeks. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Patients with FMS should receive patient education in addition to home-based exercise, which is an effective treatment for reducing symptoms, enhancing psychological well-being, and improving quality of life. |
| 6. | Computed Tomographic Analysis of the Anatomical Parameters of the Ideal Screw Trajectory Line for Laminar Screw Fixation of the Lumbar Isthmus Burhan Oral Güdü, Suna Dilbaz doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.55264 Pages 29 - 35 INTRODUCTION: Assessment of laminar anatomical parameters required for rigid fixation of the lumbar isthmus with intralaminar screws using computed tomography (CT). METHODS: Retrospective lumbar CT scans of 36 adult patients were analyzed. The parameters of the ideal laminar screw trajectory line required for isthmic defect fixation were determined using 3D multiplanar reconstruction, and linear and angular parameters were measured. The laminar screw length (LSL), the width of the thinnest part of the lamina (LW), the transverse distance of the screw entry into the lamina relative to the midline (TD), sagittal (SA) and coronal (CA) screw application angles were evaluated bilaterally at all lumbar levels. RESULTS: The mean age of the patients was 22 years. The LSL had similar values at the levels L1–3 (35–36 mm), with a slight decrease at L4 and L5 (33–32 mm). The LW increased from L1 to L4 (7–9 mm), with a slight decrease observed at L5 (8 mm). The TD increased steadily from L1 to L5 (56–10 mm). The SA was similar at L1–3 (23°–25°), with a marked increase toward L4 and L5 (30°–40°). The CA increased consistently from L1 to L5 (6°–20°). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: For rigid intralaminar screw fixation, optimal angular and linear screw application parameters should be carefully reviewed in preoperative CT studies to increase the laminar cortical bone attachment of the screw and prevent potential neurologic injury. |
| 7. | Comparing Pressure Control and Volume Control Ventilation in Obese Patients Undergoing Sleeve Gastrectomy Enes Uslu, Engin Ihsan Turan, Ayça Sultan Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.40469 Pages 36 - 43 INTRODUCTION: Obesity is a chronic, multisystemic disease associated with various comorbidities, complicating anesthesia management. This study compares the effects of pressure control ventilation (PCV) and volume control ventilation (VCV) on hemodynamic, respiratory, and blood gas parameters in patients undergoing sleeve gastrectomy. METHODS: This randomized, prospective, single-blinded study included 44 patients aged 18–65 years with a BMI>40 kg/m² (ASA III). Patients were randomly divided into two groups to receive either PCV or VCV during the operation. Key parameters, such as heart rate, mean arterial pressure, peak and plateau pressures, PEEP, lung compliance, and arterial blood gas values, were measured at regular intervals. PEEP adjustments were made according to oxygenation needs, and end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) levels were continuously monitored, with adjustments made to maintain EtCO2 within the target range of 30–40 mmHg. RESULTS: Heart rate, mean arterial pressure, peak and plateau pressures, and lung compliance were similar between PCV and VCV groups. PCV showed higher PEEP at 45 and 75 minutes, lower pH at 45 minutes, and higher PaCO2 at 45 minutes. Lactate levels showed no differences across time points. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Both PCV and VCV maintain stable hemodynamic and respiratory conditions in obese patients undergoing sleeve gastrectomy, with PCV showing higher PEEP levels and transient differences in pH and PaCO2. These findings indicate that both PCV and VCV are effective ventilation methods for sleeve gastrectomy. However, individualized patient management and close monitoring of ventilation parameters remain essential. |
| 8. | Early ECG Patterns in Acute Cerebrovascular Events: A Prospective Study Correlating Clinical Findings with Mortality and Medico-Legal Considerations Shailendra Kumar Pandey, Rajiv Ratan Singh, Sachin Kumar Tripathi, Pradeep Kumar Yadav doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.99609 Pages 44 - 50 INTRODUCTION: Acute cerebrovascular events (CVE), such as strokes, often manifest with early electrocardiographic (ECG) changes. These ECG patterns can provide crucial insights into the patient's prognosis and are essential in medico-legal cases. Understanding the correlation between these early patterns and patient outcomes, especially mortality, is vital for improving care and providing forensic clarity. To assess early ECG changes in patients with acute cerebrovascular events, correlating clinical findings with mortality, and exploring their medico-legal implications. METHODS: This hospital-based prospective study involved 100 patients admitted with acute stroke to the Medical Intensive Care Unit and Medicine Department at a tertiary care center from 2020 to 2021. Participants were selected through simple random sampling, ensuring equal inclusion chances. Data were collected within 24 hours of admission, including ECGs, clinical histories, and demographic details, and analyzed using SPSS. RESULTS: The study highlighted critical medico-legal implications, finding that 78% of 100 patients with acute cerebrovascular events exhibited ECG changes. Notably, 89% of hemorrhagic stroke patients showed abnormalities. Statistical analysis revealed significant correlations between early ECG findings and clinical se-verity, with a Chi-square value of ᵪ² = 13.14 (p=0.001396). At the same time, mortality differences based on ECG status were not statistically significant (p=0.079). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: This study emphasizes the importance of early ECG abnormalities in acute cerebrovascular events, linking them to clinical severity and mortality. Findings suggest a higher mortality rate in patients with abnormal ECGs, but further research is necessary to strengthen these associations and improve care. Medico-legal aspects involve the timely interpretation of ECGs, ensuring informed consent, accurate record-keeping, and maintaining accountability to prevent negligence and malpractice. |
| 9. | Assessing Physical Activity in Obese Children: Reliability and Validity of the PAQ-C Mehmet Eltan, Tarık Kırkgöz doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.73745 Pages 51 - 55 INTRODUCTION: In pediatric populations, the relationship between obesity and physical activity (PA) is influenced by genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and lifestyle behaviors. Despite the benefits, many children fail to meet recommended PA levels. This study aimed to determine the reliability and validity of the PA Questionnaire for Older Children (PAQ-C) and explore its potential applications in promoting PA among obese children. METHODS: 272 children and adolescents (148 obese patients and 124 healthy controls) were enrolled in this study. Descriptive statistical analysis was performed, and Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was calculated to assess the reliability of the PAQ-C. RESULTS: The mean ages of the obese and control groups were 12.1±2.2 and 12.6±1.7 years, respectively. The average BMI SDS was 2.7±0.6 for the obese group and -0.2±1.0 for the control group. No significant difference in overall PAQ-C scores was found between the two groups (p=0.252). Notable findings included lower scores among obese children in spare time and recess activities. Additionally, lower scores in self-reported statements and overall life satisfaction were observed among obese children, although these differences were not statistically significant. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.85 for the obese group and 0.86 for the non-obese group, indicating high reliability. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: The PAQ-C is a reliable and valid tool for assessing PA levels in obese children, with potential applications in promoting PA. Using the PAQ-C, researchers, and practitioners can develop targeted interventions to increase PA levels and improve health outcomes among children |
| 10. | Clinical and Treatment Management of Infantile Hemangiomas Hüseyin Avni Solgun, Özlem Terzi, Mustafa Özay doi: 10.14744/cm.2025.24855 Pages 56 - 62 INTRODUCTION: The majority of infantile hemangiomas (IHs) require observational follow-up, but for patients requiring treatment, the last decade has revolution-ized treatment with the discovery of propranolol. Therefore, in cases requiring treatment, it would be appropriate to refer the newborn to the pediatric hema-tology and oncology department as soon as IH is detected during the first examination. In this study, we aimed to explain the clinical features and treatment selection features in patients with IH. METHODS: A total of 25 female and 15 male IH cases who applied to our pediatric hematology and oncology outpatient clinic were included in our study. Before treatment, all patients were evaluated with routine complete blood count, biochemical analysis, abdominal ultrasonography (USG), and pediatric cardiology. The diagnosis dates, treatment start dates, birth dates, the diagnosis of the lesion, monthly measurements after the start of treatment, and the treatment started and doses were recorded in the follow-up forms of the patients. RESULTS: The average age of the patients at the start of treatment was 6.5 months (2 months–15 months). Twenty-four of the patients were under 6 months old. In the treatment of IH, these patients were started with an oral propranolol solution preparation at a dose of 1 milligram (mg)/kg/day. In tolerant patients, the dose was increased to 2 mg/kg/day after 3 days. All patients received propranolol treatment for at least 6 months. In patients who started treatment after diagnosis, at least 50% and at most >95% involution occurred in the IH dimensions. No patient had pathological findings in the hemogram and biochemistry tests performed every 2 months. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: In terms of ease of use, safety profile, and frequency of side effects, the use of oral propranolol solution was evaluated as very effective and tol-erable, especially in the 2–6 month patient group. Additionally, propranolol was found to be quite effective in IH patients who were older than 6 months and whose treatment had not been started for different reasons. To confirm the diagnosis, the diagnosis should be clarified by USG/color Doppler USG, preferably by obtaining the opinion of a pediatric radiologist before starting treatment. |
| 11. | Impact of Initial Admission Location on Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis and Management: Gynecologic vs. Adult Emergency Departments Abdussamed Vural, Turgut Dolanbay, Mustafa Oguz Cumaoglu, Nazan Ardıc, Enes Karaman, Mustafa Cihan Altay, Hayri CANBAZ doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.96630 Pages 63 - 69 INTRODUCTION: This study aimed to evaluate the impact of the initial admission clinic (Gynecologic and Obstetric emergency medicine [GOED] vs. Adult emergency medicine [AED]) on the diagnostic and therapeutic processes of ectopic pregnancy (EP). Additionally, we investigated the influence of clinic-specific factors on the treatment outcomes. METHODS: This retrospective, cross-sectional study included 164 patients diagnosed with EP between October 1, 2021, and October 1, 2023, at a tertiary hospital. Data, including demographics, clinical presentation, time to diagnosis, diagnostic tests used, treatment modality, and patient outcomes, were collected from electronic hospital records. Statistical analyses were performed to determine the relationship between the initial admission clinic and the diagnostic/therapeutic outcomes. RESULTS: Patients admitted to the GOED had significantly shorter median diagnostic times than those admitted to the AED (1 hour vs. 2.5 hours, p<0.001). The surgical intervention rate was higher in the AED group (64.7%) than in the GOED group (36.9%; p=0.004). No significant differences were found in patient out-comes or length of hospital stay based on the time of admission (working vs. nonworking hours). GOED admissions were associated with a higher proportion of outpatient management (87.5%) than were AED admissions. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Initial admission to the GOED significantly reduced diagnostic delays and increased the likelihood of noninvasive management of EP. These find-ings highlight the importance of clinic-specific expertise in optimizing EP management and reducing the need for surgical interventions. Further prospective studies are needed to validate these results and to explore the long-term impact of clinic-specific factors on patient outcomes. |
| REVIEW | |
| 12. | Endothelial Dysfunction in Women and its Relationship with Infertility Mehmet Ulaş Bilir, Hale Göksever Çelik, Ercan Baştu, Tuba Günel doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.58070 Pages 70 - 77 Endothelial dysfunction is an early indicator in the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and its evaluation in clinical settings is of great importance. Men are particularly at higher risk compared to premenopausal women, and the earlier onset of CVDs in men is associated with differences in estrogen levels between genders. Estrogen and testosterone regulate endothelial function through both genomic and non-genomic pathways, affecting vasodilation, inflammation, and cell proliferation. In women, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis are associated with endothelial dysfunction. Although the relationship between endothelial dysfunction and female sex hormones has been demonstrated, its direct impact on female fertility remains unclear. Despite the connection between endothelial health and reproductive parameters, definitive markers for fertility and infertility have yet to be identified, making their use in clinical practice challenging. The polygenic nature of reproductive health further complicates the detection of specific markers. Therefore, despite significant advancements, further research is needed to identify reliable endothelial markers for fertility and infertility. This review focuses on the significance of the gender differences in endothelial dysfunction concerning cardiovascular diseases and fertility. |
| CASE REPORT | |
| 13. | Ovarian Teratoma Torsion with CA 19-9 Elevation: Case Report Deniz Balsak, Fatma Zehra Kurnuç doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.74745 Pages 78 - 80 Ovarian torsion is a rare gynecologic emergency and causes serious medical problems. The diagnosis of ovarian torsion is not always easy. Ovarian torsion is the most common complication with a confusing ultrasonographic diagnosis. Although the demonstration of blood flow by Doppler ultrasonography does not rule out the diagnosis of ovarian torsion, a serum marker with high reliability and sensitivity in the preoperative diagnosis of ovarian torsion has not yet been defined. A 19-year-old G0P0 patient was admitted to our clinic with pelvic pain lasting 1 week. Abdominopelvic ultrasound revealed a 9 cm diameter lobulated cystic lesion in the right adnexa. Abdominopelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a 90 × 88 mm cystic lesion consisting of heterogeneous solid structures. The left ovary and other intra-abdominal structures were normal. Tumor markers were as follows: CEA: 24.90 U/mL, AFP: 40 U/mL, CA 15-3: 23.4 U/mL, CA 19-9: 383 U/mL. The patient's MRI report was suspicious for malignancy, and the diagnosis of torsion could not be clarified. As the patient’s condition progressed, laparotomy was decided upon, and a frozen examination was requested. Cystectomy was performed after the findings were compatible with a dermoid cyst. CA 19-9 is a tumor marker that is increased, especially after ovarian teratoma torsion, and may be useful in diagnosing clinical teratoma torsion. However, larger studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis. |