Quick Search
Volume: 16 Issue: 1 - 2024
| 1. | Front Matter Pages I - III |
| 2. | Editorial Mustafa Kadıhasanoğlu Page IV |
| RESEARCH ARTICLE | |
| 3. | Evaluation of the Relationship Between Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, Depression and Quality of Life Yaşar Pazır, Hüseyin Koçan, Taha Burak Bulut, Emre Arı, Semih Aktaş, Mustafa Kadıhasanoğlu doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.08370 Pages 1 - 7 INTRODUCTION: This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), depression, and quality of life (QoL). METHODS: his cross-sectional study included 312 male patients over the age of 40 who were newly diagnosed with LUTS secondary to BPH between September 2019 and October 2023. LUTS, QoL, and depressive symptoms were assessed with the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), short- form health survey (SF-36), and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) questionnaires, respectively. RESULTS: Depression was detected in 46 (15%) patients. While IPSS total score, storage and voiding subscores were found to be significantly higher in cases with depression than in those without depression, SF-36 QoL scores were significantly lower. Depressive symptoms were more severe in patients with moderate to severe LUTS (9.2±7.3 vs 6.7±6.3, p=0.011). IPSS total, voiding and storage subscores were positively correlated with BDI scores and mostly negatively correlated with QoL scores. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: This study showed that subjects with moderate to severe LUTS due to BPH had more severe depressive symptoms and a lower QoL than those who were mildly symptomatic. Increasing the severity of LUTS worsens depressive symptoms. Also, depression is associated with more severe LUTS. |
| 4. | Radiotherapy Outcomes in Adults with H3K27M-Altered Midline Gliomas and Poor Performance Status Esengül Koçak Uzel, Melisa Bağcı Kılıç, Metin Figen, Meltem Kirli Bölükbaş, Ömer Uzel doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.02411 Pages 8 - 12 INTRODUCTION: Treatment of H3K27M-altered midline gliomas is a significant challenge. This study aims to assess the efficacy of radiotherapy for these patients. METHODS: Thirteen patients with histologically confirmed H3K27M-altered midline glioma, treated with radiotherapy +/- temozolomide be- tween 2019 and 2021, were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical and radiological responses, survival times, and prognostic factors were evaluated. All patients were treated with hypofractionated radiotherapy, with a dose of 25-40 Gy. RESULTS: The median age was 42 years (ranging from 19 to 55). Karnofsky Performance Status scores ranged from 50 to 70, with a median score of 50. Hypof- ractionated radiotherapy was administered to all patients, with 25 Gy given in 5 fractions to 7 patients (53.8%), 39 Gy in 13 fractions to 3 patients (23.1%), and 40 Gy in 15 fractions to 3 patients (23.1%). Clinically, two patients (15.4%) showed symptomatic improvement, five patients (38.8%) remained stable, and six patients (46.2%) had neurological deterioration. Radiologically, one patient had a partial response, six patients (46.2%) had stable disease, and radiological progression occurred in three patients (23.1%). The median progression-free survival and median overall survival time were 123 and 154 days, respectively. Karnofsky Performance Status 50 was associated with a worse prognosis. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: These results suggest that the efficacy of radiotherapy might be limited for adults with H3K27M-altered midline gliomas with poor performance status. New studies are necessary for a more comprehensive understanding of effective therapeutic strategies. |
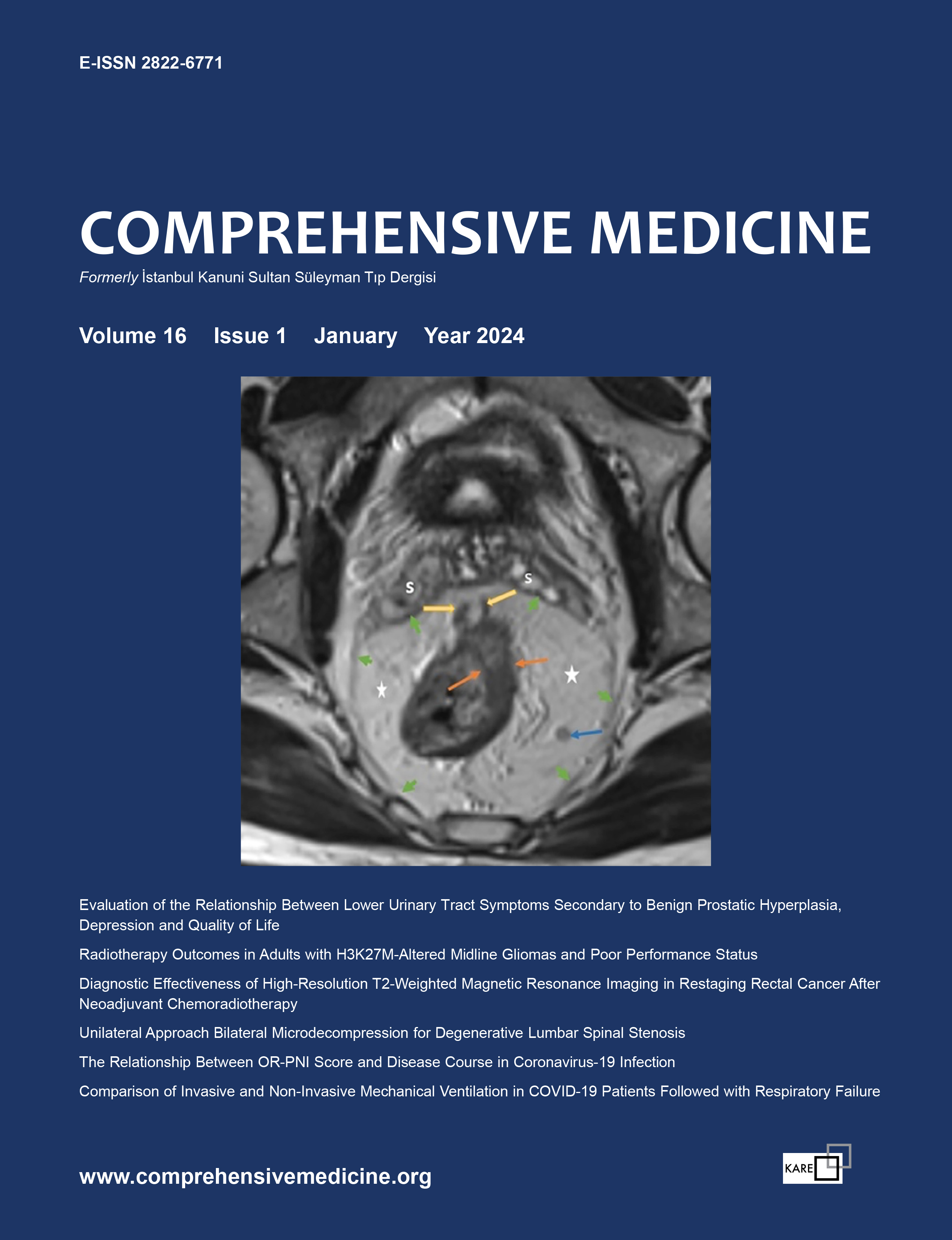
| 5. | Diagnostic Effectiveness of High-Resolution T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Restaging Rectal Cancer After Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Ümmihan Topal, Hakan Yırgın, Nermin Gündüz, Yasin Kara, Serhan Yılmaz, Erkan Somuncu, Gülseren Yılmaz, Ayça Sultan Şahin, Ali Kocataş doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.07269 Pages 13 - 18 INTRODUCTION: The staging of rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) influences treatment planning. It is critical to have an accurate and practical radiological identification. The technical success of a high-resolution T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (hT2W-MRI) sequence in restaging locally progressed rectal cancer treated with nCRT was investigated in this study. METHODS: The study included 19 patients (mean age=56, range=37–76) who had rectal cancer surgery between 2020 and 2022, a rectum MRI, and nCRT. Following surgery, MRI data were compared to relevant histological studies. RESULTS: hT2W-MRI correctly predicted all cancers with pathological stage T3 (100%, 5/5). Three out of four patients (75%) with pathological stages T4a and T4b were correctly predicted by hT2W-MRI. When lymph node positivity was taken into account, the hT2W-MRI prediction rate was 42.1% (8/19). All tumors with a circumferential resection margin (CRM), peritoneal reflection involvement, and extramural venous invasion were appropriately predicted by hT2W-MRI. hT2W-MRI had a good success rate in predicting pathological response (residual tumor) (89.5%, 17/19). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Incorporating the hT2W-MRI sequence into routine pelvic MRI examination sequences can be beneficial for detecting residual tumor and staging rectal cancer after nCRT. |
| 6. | Unilateral Approach Bilateral Microdecompression for Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Luay Şerifoğlu, Mustafa Umut Etli doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.46220 Pages 19 - 23 INTRODUCTION: Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis is a frequent cause of back and leg pain in elderly patients. Degenerative spinal stenosis may be due to inter- vertebral disk bulging, joint facet hypertrophy, thickening of the ligamentum flavum, and spondylolisthesis. The aim of this study is to investigate the results of unilateral approach bilateral microdecompression for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis patients. METHODS: We observed 78 patients who have back and/or leg pain with neurogenic claudication. The patients were scored by visual analog scale (VAS), oswestry disability index (ODI) score, and walking distance (WD). The surgical technique used in all stenotic levels was unilateral approach bilateral microdecompression. All patients were questioned and examined before surgery, post-operative 2nd year. RESULTS: Thirty-nine males and 39 females total of 78 patients with the mean age of 64.3±7.2 were investigated. There was no statistically significance accord- ing to gender and age. Pre-operative mean VAS, ODI and WD values were 8.9±1.1, 65±17.20, 42±21.30 and post-operative 2nd year values were 1.2±0.23, 17±1.91, 1800±617.13. All three parameters were found statistically significant when compared between pre-operative and post-operative values (p<0.05). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: The results of the unilateral approach bilateral microdecompression for treating lumbar spinal stenosis are satisfying because you can achieve sufficient decompression with minimal invasive technique without dissecting and damaging the opposite side tissues. |
| 7. | The Relationship Between OR-PNI Score and Disease Course in Coronavirus-19 Infection Mitat Türker, Iskender Ekinci, Yılmaz Önal, Hanişe Özkan, Betül Türker, Ahmet Çınar, Irem Kıraç Utku, Gülden Anataca, Ömür Tabak, Murat Akarsu doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.30974 Pages 24 - 31 INTRODUCTION: Prognostic nutritional index (PNI), fibrinogen/albumin ratio index (FARI), and OR-PNI scores (obtained by using the PNI score, oxygen saturation, and computed tomography findings) were examined. METHODS: This study was conducted with 486 patients. RESULTS: A FARI score of >18.08 predicted mortality with a sensitivity of 71.8% and a specificity of 71.1%. In the receiver operating characteristic analysis for PNI and OR-PNI scores, p-values were <0.001, but the area under the curve values were found to be 0.151 and 0.072, respectively. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: FARI score is a parameter that predicts mortality; PNI and OR-PNI failed to predict mortality. In addition, PNI and OR-PNI values were found to be closely related to the course of the disease. |
| 8. | Comparison of Invasive and Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation in COVID-19 Patients Followed with Respiratory Failure Döndü Genç Moralar, Ülkü Aygen Türkmen, Osman Çelik, Aleaddin Uluç, Serpil Şehirlioğlu Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.14632 Pages 32 - 38 INTRODUCTION: The most important complication associated with coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) is respiratory failure, which requires mechanical ventilation. The aim of our study is to evaluate the effectiveness of the use of invasive and non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIV) on oxygenation in patients with COVID-19 who had respiratory failure and needed ventilation support. METHODS: According to the ventilation support used, the patients were divided into two groups: Those for whom NIV was initially preferred (n=48) and those who were initially intubated and received invasive mechanical ventilation (n=50). Arterial blood gas analyzes of the patients were evaluated. The changes in oxygenation and ventilation, the incidence of complications such as hypotension and hypertension, and mortality rates were compared. RESULTS: The partial arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2) values were similar during the follow-up of the patients who were initiated on treatment with NIV and those who were initiated on treatment with invasive mechanical ventilation. However, the survival rate was higher in the patients who were initiated on treatment with non-invasive mechanical ventilation. It was remarkable that the partial arterial carbon dioxide pressure value was higher in the invasive mechanical ventilation group than in the NIV group. The incidence of complications such as hypotension or hypertension was less in the non-invasive mechanical ventilation group. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Although PaO2 values are similar, it was found that the survival rate was higher and the complication rate was lower in the patients for whom NIV was preferred. Therefore, we think that NIV should be preferred as much as possible. |
| 9. | The Effects of Colchicine Treatment on Cardiac and Inflammatory Markers in COVID-19 Patients Followed Up in Intensive Care Unit Mikail Akın, Kadir Arslan, Ebru Kaya, Ayça Sultan Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.88597 Pages 39 - 44 INTRODUCTION: It has been stated that colchicine can reduce the cytokine storm and inflammation in cardiac myocytes during COVID-19 infection. This study aims to investigate the effect of colchicine treatment on cardiac and inflammatory markers in COVID-19 patients followed in the intensive care Unit (ICU) of a tertiary center. METHODS: Patients followed up in the ICU with the diagnosis of COVID-19 between April 2020 and June 2020 were evaluated retrospectively. Patients who received standard treatment in moderate-to-severe COVID-19 patients were analyzed by classifying them as the control group and patients who were added to the standard treatment within the first 48 h as the colchicine group. RESULTS: A total of 79 patients, 39 in the colchicine group and 40 in the control group, were included in the study. Demographic data and the presence of comorbid disease were similar between groups. The mean length of stay in the ICU was 19.4±8 days in the colchicine group and 14.7±7 days in the control group. The length of stay in the ICU was found to be significantly higher in the colchicine group (p=0.017). There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of C-reactive protein, Interleukin-6, troponin T and D-dimer levels, and 28-day mortality (94.9% vs. 95%, p>0.05). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Adding oral colchicine to the standard treatment within the first 48 h after hospitalization in moderate-to-severe COVID-19 patients followed in the ICU did not improve the clinical status of the patients. It did not reduce cardiac and inflammatory markers and mortality rates. |
| 10. | Pediatric Surgeons' Approaches to Postoperative Analgesia in Türkiye Ela Erten, Gökhan Berktuğ Bahadır doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.19480 Pages 45 - 50 INTRODUCTION: This research aimed to evaluate the knowledge and experience of pediatric surgeons in Türkiye regarding multimodal analgesia approaches, and the use of regional anesthesia techniques in pediatric abdominal surgery. The research also aimed to investigate what can be done for better pain management in pediatric abdominal surgeries in Türkiye. METHODS: The study sample included 825 active pediatric surgery specialists and 204 resident physicians in Türkiye. A questionnaire consisting of 27 questions was distributed to Turkish pediatric surgeons via email and WhatsApp. Based on the answers given to the questionnaire, we aimed to investigate the most commonly used postoperative analgesia methods in pediatric abdominal surgeries, whether multimodal analgesia methods are preferred for pain control, and the reasons affecting these preferences. RESULTS: Feedback was received from 122 physicians. Among the participants, 54.09% had worked as pediatric surgeons for 15 years or more, while 8.19% were resident physicians. Anesthesiologists, with whom 55.4% of the participants worked, preferred only intravenous (IV) drugs as the postoperative analgesia method. It was found that 70.8% of the participants did not experience ultrasound-guided anterior abdominal wall blocks in pediatric cases at their institutions. Additionally, a significant proportion of the participants (82%) reported a lack of training on multimodal analgesia. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: The data show a lack of awareness regarding the importance of using multimodal analgesia approach in pediatric cases, revealing the importance of the benefits of collaborative work and training programs. |
| 11. | Clinical Characteristics, Antibiotic Resistance Profiles, and Factors Affecting Mortality in Patients Isolated Acinetobacter Baumannii in Intensive Care Unit: Retrospective Tertiary Center Analysis Kadir Arslan, Ayça Sultan Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.57338 Pages 51 - 57 INTRODUCTION: Acinetobacter baumannii is an important opportunistic pathogen that can cause severe septicemia and mortality. This study aims to investigate the antibiotic resistance profiles of patients isolated from A. baumannii in the intensive care unit (ICU) and the factors affecting mortality. METHODS: Patients who were followed up in a tertiary ICU between January 2020 and January 2023 and who were found to have A. baumannii in various clinical samples were included in the study. The patients were divided into the mortality group (Group M) and the survival group (Group S). Their clinical features, antibiotic resistance profiles, and mortality factors were analyzed. RESULTS: A total of 228 patients, 110 (48.2%) in Group M and 118 (51.8%) in Group S, were included in the study. The median age of the entire population was 67.5 (18–96), and 60.1% were male. A. baumannii strains were most commonly (59.2%) isolated from tracheal aspirate and sputum cultures. Resistance to carbapenems was 94.2–96.8%, aminoglycosides 88.5–99.2%, tigecycline 54.6%, and colistin 8.1%. Group M had significantly higher Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation-2 (APACHE-2) scores, mechanical ventilation requirements, and multidrug-resistant A. baumannii count. Independent risk factors for mortality were determined by APACHE-2 scores and mechanical ventilator application at the time of admission to the ICU. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: We think that in A. baumannii infections, which are highly resistant to many antibiotics and have high mortality rates, determining the risk factors indicating mortality and antibiotic resistance profiles and making treatment plans will contribute to the prognosis of the patients. |
| REVIEW | |
| 12. | The Comorbidity of Specific Learning Disorders in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Şennur Günay Aksoy doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.30602 Pages 58 - 62 Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurobiological disorder that begins in childhood, with symptoms continuing throughout life, negatively impacting an individual’s cognitive, social, and academic functioning. Specific learning disability (SLD) is a developmental disorder characterized by its initial signs being noticeable during the preschool years. The broad category of SLD encompasses various skill deficits, but the most common symptoms are typically divided into three broad subcategories: reading disorder, written-language disorder, and mathematics disorder. Generally, there is an estimated comorbidity rate between SLD and ADHD ranging from 31% to 45%. While ADHD is conventionally defined as an externalizing disorder, children with this condition often exhibit learning difficulties and academic problems in addition to behavioral issues such as impulsivity, oppositional behavior, and conduct problems. These academic difficulties are frequently overlooked, as behavioral problems, often linked to impulsivity, tend to take precedence. The purpose of this review is to draw attention to these overlooked areas of concern in children diagnosed with ADHD, both in clinical practice and academic literature, and to review relevant literature studies. |
| RETRACTION | |
| 13. | RETRACTION: Analysis of the Knowledge Level of the Surgical Residents Regarding the Pre-Operative Assessment of the Adult Elective Non-Cardiac Surgery Patients with Specific Clinical Conditions Gözde Altun, Murat Aksun, Ayça Sultan Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2024.79553 Page 63 Retraction Notice This article is retracted from publication by decision of Editor upon the authors’ request: Altun G, Aksun M, Şahin AS. Analysis of the Knowledge Level of the Surgical Residents Regarding the Pre-Operative Assessment of the Adult Elective Non-Cardiac Surgery Patients with Specific Clinical Conditions. CM 2023;15(2): 96-101. DOI: 10.14744/cm.2023.49092 |