Quick Search
Volume: 15 Issue: 2 - 2023
| 1. | Front Matter Pages I - III |
| OTHER | |
| 2. | Editorial Mustafa Kadıhasanoğlu Page IV |
| RESEARCH ARTICLE | |
| 3. | Analysis of Clinical Outcomes of the ARDS Patients in the Intensive Care Unit Ebru Kaya, Nazan Yıldız, Ayça Sultan Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.54264 Pages 91 - 95 INTRODUCTION: During the follow-up of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients in intensive care units (ICU), there are many changing parameters such as clinical findings, vital signs, laboratory values, and treatment. In this article, we analyzed some data of some ARDS patients that we followed in our ICU, on the 1st day of admission to our ICU and the last day when they were discharged from our ICU (departure to the ward or exitus). METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed 32 ARDS patients followed in our ICU in the tertiary ICU between January 2015 and January 2020. RESULTS: Glasgow coma scale (GCS), heart rate (HR), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and albumin median levels were compared at the first admission and dis- charge from ICU. There was statistically significant difference between admission and discharge values of GCS, HR, MAP, and albumin. Analysis of laboratory findings including PCO2, lymphocyte, total bilirubin, sodium, APTT, and lactate also showed meaningful difference according to admission levels. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Clinical findings, vital signs, laboratory values, and treatment during the follow-up of patients in ICU s with ARDS are still not sufficient. Therefore, de- termining the clinical findings, vital signs, and some laboratory values in terms of the course of ARDS are very important for the follow-up and treatment of patients. |
| 4. | Analysis of the Knowledge Level of the Surgical Residents Regarding the Pre-Operative Assessment of the Adult Elective Non-Cardiac Surgery Patients with Specific Clinical Conditions Gözde Altun, Murat Aksun, Ayça Sultan Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.49092 Pages 96 - 101 INTRODUCTION: We aimed to analyze the knowledge level of the surgical residents regarding pre-operative assessment and increase their collaboration with other teams in optimizing general medical status of the patients to reduce the duration of hospital stay and complication rates. METHODS: Our study was conducted with the residents of eight surgical divisions in our institution. Eighty surgical residents enrolled in the study. The 2018 update of the European Society of Anesthesiology (ESA) was used during the preparation of the survey questions. The questions were catego- rized based on the specific clinical conditions and medications noted in the ESA guideline. Answer choices were “correct”, “wrong,” or “no idea.” RESULTS: Sixty-five (81.2%) of the respondents were male and 15 (18.8%) were female. Analysis of distribution of the mean correct answer rates (%) revealed that the question regarding “herbal medications” led to the lowest correct answer (13.75%), while the category “bridging and anticoagulation” was associated with the highest (72.5%) correct answer. Total mean correct answer was calculated as 50.8%. There was no significant correlation between the residents’ seniority level (i.e., postgraduate year) and their correct answer rates in neurosurgery, general surgery, ear-nose-throat (ENT), and plastic surgery divisions. However, there were statistically significant differences in ophthalmology, urology, orthopedic surgery, and obstetrics and gynecology divisions. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: The general medical status of the patients should be optimized to reduce the risk of complications. To achieve this goal, surgical residents should collaborate with the other teams in each perioperative stage. In addition, we suggest that the curriculum be reviewed to increase the knowledge level of the surgical residents regarding pre-operative care. |
| 5. | Does Pre-operative TSH Level Affect Pathological Findings in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma? Erkan Somuncu, Nezihe Berrin Dodur Önalan doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.78045 Pages 102 - 106 INTRODUCTION: Although thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is known to induce thyroid malignancies, the relationship between pre-operative TSH and patho- logical findings has not been thoroughly evaluated. This study aimed to assess the relationship between pre-operative TSH levels and pathological findings. METHODS: The records of 156 patients (135 women and 21 men) operated for papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) between January 2017 and June 2020 were retrospectively reviewed and divided according to TSH level 2.5 mIU/L above (50 patients) and below (106 patients). The relationship between pre-oper- ative fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) result, pathological findings, tumor diameter, multicentricity, lymphovascular invasion, extrathyroidal extension, capsule invasion, and neck (central, lateral) metastasis were compared for pre-operative TSH levels. RESULTS: There was no significant difference between pre-operative TSH level and lymphovascular invasion, extrathyroidal extension, central and lateral lymph node metastasis, primary tumor size, and multifocality. However, TSH levels were found to be significant above 2.5 mIU/L in patients with capsule invasion positivity (p=0.007). TSH levels were significantly lower in our patients with malignant or suspected FNAB (p=0.015). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Although pre-operative high TSH levels tend to be more common malignant in the literature, malignancy and suspected FNAB results are ob- tained in low TSH levels. TSH level should be considered as an independent factor in preoperative diagnosis, and thyroid malignancies should be suspected in cases with a TSH level below 2.5 mIU/L. |
| 6. | Evaluation of Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Seroprevalence in People Living with HIV Ayşe Serra Özel, Lütfiye Nilsun Altunal, Merve Çağlar Özer, Şevval Özen Aksakal doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.47966 Pages 107 - 111 INTRODUCTION: Due to the common transmission routes, hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) coinfections are common in people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLWH). We planned to investigate the frequency of HBV and HCV coinfection in PLWH. METHODS: In this single-center, retrospective, and observational study, 277 PLWH were evaluated between January 2016 and August 2022 in a Training and Research Hospital, in Türkiye. RESULTS: The median age of patients was 42±13 years, and 84.8% were male. Nine patients (3.2%) were found to be positive for HBsAg, 11 (3.9%) were positive for isolated anti-HbcIgG, 65 (23.5%) were both positive for anti-HBcIgG and anti-HBs, and 102 (36.8%) were immunized with the hepatitis B vaccine (positive for Anti-HBs). Four of the HBsAg-positive patients were diagnosed with acute hepatitis B clinic during the emergency admission. HBV DNA levels were unde- tectable in admission and follow-up among the patients with isolated anti-HBcIgG positivity. Three patients were anti-HCV-positive and HCV RNA levels were negative in two patients. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: HIV infection accelerates the progression of hepatitis B/C-related liver disease due to immunosuppression. It is important to detect and follow-up on HBV/HCV serologic markers in these patients’ groups. |
| 7. | Procedural Sedation Protocols with or without Ketamine in Pediatric Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: A Retrospective Cohort Study Naime Yalçın, Nurdan Kamilçelebi, Ayça Sultan Şahin, Barış Sandal, Abdurrahim Derbent, Ziya Salihoğlu doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.47965 Pages 112 - 119 INTRODUCTION: A considerable difference exists in pediatric endoscopy sedation practices with the optimal sedation protocol for gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy a subject of controversy and to investigate the safety and efficacy of sedation protocols with or without ketamine in procedural sedation for pediatric GI endoscopy. METHODS: A total of 78 pediatric patients who received sedation anesthesia for GI endoscopy were included in this retrospective study. Anesthe- sia parameters include duration time, doses of anesthetic agents, Ramsay sedation score, respiratory and hemodynamic parameters, recovery time, modified Aldrete recovery scores, and side effects. Study parameters were evaluated with respect to ketamine dose (no ketamine group (NKG), low-dose ketamine group (LDKG, ≤0.75 mg/kg), and high-dose ketamine group (HDKG, ≥1 mg/kg). RESULTS: The upper GI endoscopy rate (58.12% vs. 90.0%, p=0.001) was significantly lower in LDKG versus HDKG. No significant changes were observed in blood pressure levels, oxygen saturation, or heart rate compared to baseline levels. No significant difference was noted between study groups in terms of recovery time, modified Aldrete recovery scores, and nausea/vomiting. Final Ramsay sedation scores were significantly higher in NKG (p<0.05) and LDKG (p<0.01) than in HDKG. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Our findings indicate a favorable safety and efficacy profile for ketamine as a useful adjunct to procedural sedation for pediatric GI endoscopy, enabling better quality of sedation with a low risk of cardiorespiratory suppression, or serious complications. |
| 8. | Immunological Risk Monitoring in Patients with High Immunologic Risk and Its Effects on Clinical Outcomes Zuhal Atan Uçar, Ayşe Sinangil, Mustafa Emre Özçilsal, Yener Koç, Alaattin Yıldız, Emin Barış Akın doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.82084 Pages 120 - 124 INTRODUCTION: In this study, it was aimed to follow up the immunological risk of patients with high immunological risk and to determine the effect of desensitization treatment in these patients. METHODS: Living donor transplantation patients with panel reactive antibody (PRA), donor specific antibody (DSA), and/or single antigen bead test positivity and retransplantation patients were included in the study. PRA and/or DSA levels of pre-transplant and post-transplant period were evaluated in all patients. We compared follow-up of immunological data and clinical outcomes of patients who had desensitization (Group 1) versus who did not (Group 2). RESULTS: Totally 117 patients were included in this study. Thirty-four patients had desensitization treatment. There was no statistically difference between the groups based on age, hepatitis serology, history of blood transfusion, pregnancy, history of dialysis, and acute rejection episodes (p>0.05). Female gender was higher in Group 1 patients (p<0.05). HLA-MM, PRA Class 2, DSA Class 2 levels were higher in Group 1 in pre-transplant period (p<0.05). During the follow-up period, it was determined that the patients in Group 1 had significantly lower PRA Class 2 values at the 1st month and DSA Class 2 values at the 1st and 3rd months compared to the pre-transplant period (p<0.05). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Immunological risk decreases with desensitization therapy in the patients with high immunological risk. This decrease is more distinctive in the first 3 months of post-transplant period in which acute rejection attacks are more common. |
| 9. | Diagnostic Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Diagnosing Acute Cholecystitis Kemal Şener, Adem Çakır, Hüseyin Kılavuz, Serkan Doğan, Ramazan Güven, Semih Korkut doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.18209 Pages 125 - 131 INTRODUCTION: Acute cholecystitis (AC) is an acute inflammatory disease of the gallbladder. Although there are algorithms used today in the diagnosis of AC, there is still a need for inexpensive and fast diagnostic parameters. The systemic immune-inflammation index (SIII) is a novel prognostic indicator of systemic inflammation. In our study, the prognostic value of SIII in the differential diagnosis of AC was investigated. METHODS: Our study was designed as a retrospective single-center study. The study was conducted with 150 patients who were admitted to the emergency department with abdominal pain and diagnosed with AC and a control group of 150 patients not diagnosed with AC. RESULTS: In our results, the white blood cell, neutrophil, and C-reactive protein mean values were found to be statistically significantly higher in the study group than in the control group. Once the cutoff value was established at 743.92 (×109 /dL), the SII was found to have a sensitivity of 70% and a specificity of 59.2% in the diagnosis of AC. This assessment was also performed for neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and with a cutoff value of 2.91, it had a sensitivity of 62% and a specificity of 61.3%. There was no significant relationship between the Gangrenous cholecystitis (GC) and non-GC groups in terms of the diagnostic value of SIII. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: The present study found that the SIII is an index that can be used in the diagnosis of AC but be unsuccessful in distinguishing between GC and non-GC types. |
| 10. | The Effect of the Full Closure Process on the Patient Density in the Emergency Department Gökhan Yılmaz, Ahmet Uyanık, Ismail Aktaş, Murat Akıncı, Hasan Gazi Uyar doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.02486 Pages 132 - 137 INTRODUCTION: Social isolation methods are one of the important steps in the prevention of viral pandemics. In this study, we aimed to determine the impression of the full closure process, which is one of the social isolation methods, on the emergency department patient density and the operation of the emergency department. METHODS: Patients who admitted to Konya Meram Public Hospital between April 14, 2021, and June 01, 2021, with coronavirus disease 2019 symptoms and signs were included in the study. Three periods were established for the study: The pre-full closure period, the full closure period, and the post- full closure period. The number of daily admissions to the emergency department, the number of patients hospitalized from the emergency department to the pandemic service or the pandemic intensive care unit, and the total number of hospitalizations were recorded for these three periods. RESULTS: The information data of 7891 patients who come into the emergency department between the specified dates were included in the study. The differ- ence between all patient groups was found to be statistically significant as a result of the statistical analyzes made with the number of daily admissions to the emergency department, the number of patients hospitalized from the emergency department to the pandemic service or the pandemic intensive care unit, and the total number of hospitalizations (p=0.001). DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: We concluded that the full closure process contributes to the reduction of emergency department patient density in viral pandemics. We think that social isolation should be considered in order not to disrupt the functioning of the hospital, especially in the emergency departments, in viral pandemics that may be seen in the future. |
| 11. | qSOFA Scores Versus SIRS Criteria and SOFA Scores for Sepsis in the Emergency Department; A Prospective, Observational, and Cohort Study Hanife Bilgili, Fatih Çakmak, Afşın İpekci, Yonca Senem Akdeniz, Türker Demirtakan, Ibrahim Ikizceli doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.68916 Pages 138 - 142 INTRODUCTION: Sepsis is a syndrome of physiologic, pathologic, and biochemical abnormalities that is induced by infection. Sepsis constitutes 5,2% of total hospital and 0,4% of emergency department admissions, and has high mortality rates (as high as 28%). METHODS: In the application to the emergency department, patients’ comorbid disorders and demographic information indicated by patients and their relatives; blood pressure, pulsation, body temperature, respiratory rate, white blood cell count, platelet count, bilirubin level, creatinine level, urine output; and GCS score, SIRS criteria, SOFA and qSOFA scores and culture results were saved to the form prepared for the study. RESULTS: 59% of the patients were male and 41% of them were female. Mean age of the patients was 62,25±16,48 years. According to diagnosis, SIRS criteria and SOFA scores had higher sensitivity rate than qSOFA scores. According to the mortality, SOFA score had highest sensitivity and NPV, qSOFA had highest specificity and PPV. SIRS criteria, SOFA and qSOFA scores and mortality rate were examined, there was a moderate positive relationship (r=0.44) only between SOFA scores and mortality rate. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: As a result it was concluded that usage of qSOFA scores is more optimal in emergency department for giving fast decision. However it was found that the qSOFA scores have low sensitivity for diagnosis and prediction of the mortality. |
| 12. | An Experimental Study for Ki67 in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Single-center Experience Erkan Somuncu, Alper Koçbıyık, Hakan Bölükbaşı, Yasin Kara, Mehmet Celal Kızılkaya, Mustafa Uygar Kalaycı doi: 10.14744/cm.2022.01069 Pages 143 - 147 INTRODUCTION: The objective of this study was to determine the role of Ki67 expression level in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). METHODS: This is a retrospective study of patients undergoing a thyroidectomy. A total of 150 PTC or benign thyroid disease patients were retrospectively analyzed. Cytological and immunohistochemical evaluations of Ki67 were based on the material, obtained by fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Proliferative activity was immunohistochemically assessed. The obtain ki67 values were compared with the postoperative pathological findings. Other clinico- pathological factors were identified through statistical analyses. RESULTS: There were 86 patients in the PTC group and 74 patients in the benign group (thyroid adenomas, nodular thyroid disease, and thyroiditis). One hundred and thirty-five of the patients were female and 15 were male. The median age was 48 years (range 29–74). The Ki67 expression level in the PTC group was significantly higher than benign thyroid disease group (p=0.010). The cutoff value for Ki67 in ROC analysis was determined as 31.2 (%) with a sensitivity of 67.4% and a specificity of 62.2% (area under the curve: 0.668). However, there was no significant relationship between Ki67 expression level in the PTC group and clinicopathological factors. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Ki67 may be a useful biomarker in distinguishing PTC from benign thyroid disease. Nevertheless, longer follow-up studies with large samples are needed to better determine the relationship between Ki67 and clinicopathological findings. |
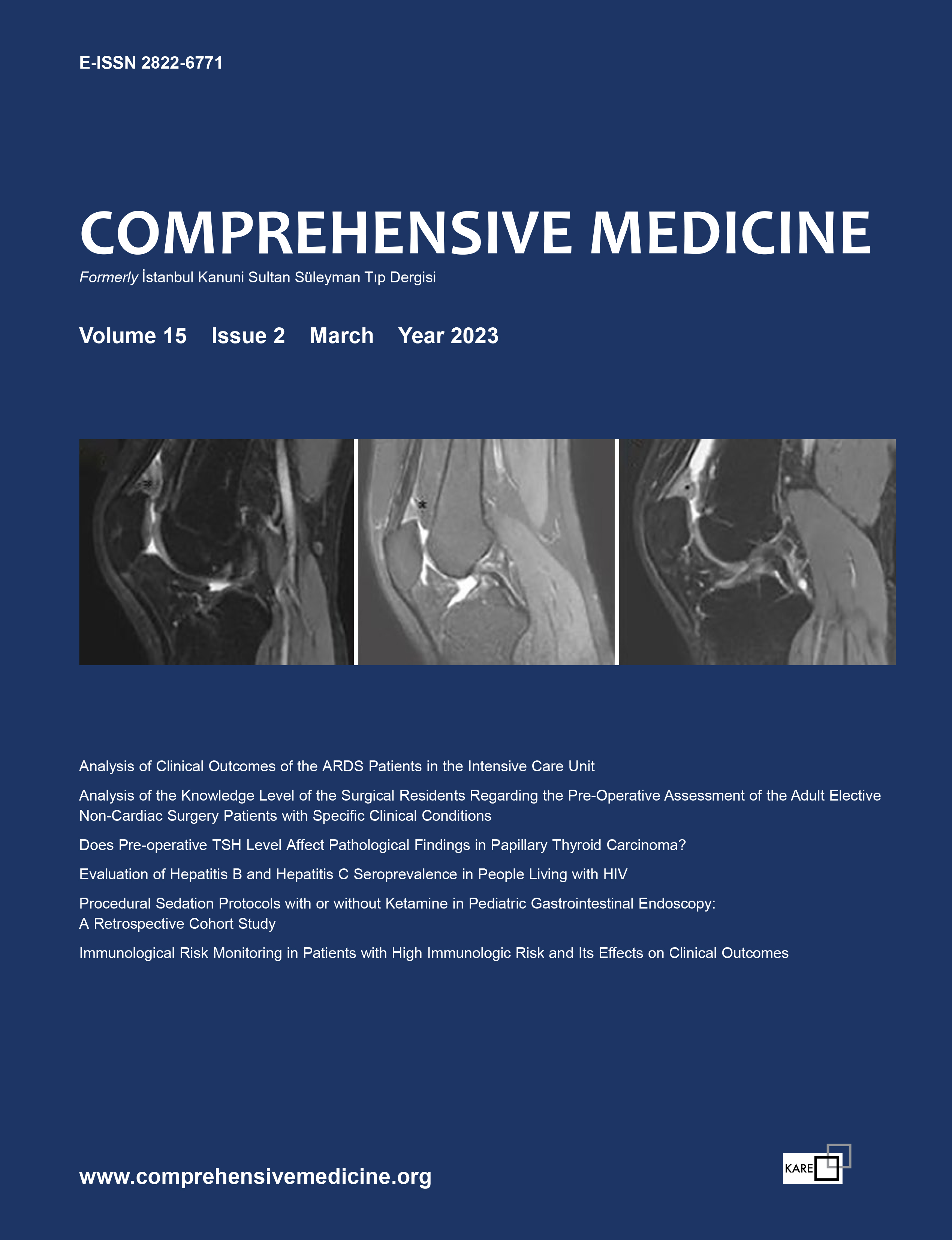
| 13. | Clinical Significance of Quadriceps Fat Pad Edema: Its Relation with Anterior Knee Pain and Other Patellofemoral Joint Pathologies Aysu Başak Özbalcı, Cihan Kalkan doi: 10.14744/cm.2022.92499 Pages 148 - 155 INTRODUCTION: This study aimed to determine the frequency of edematous changes seen in QFP among patients undergoing MRI due to anterior knee pain (AKP) and to elucidate the relation between such changes and other patellofemoral joint pathologies. METHODS: In this retrospective case–control study, individuals with (n=340) and without (n=350) AKP undergoing MRI between January 2018 and January 2020 were evaluated. All images were examined for the presence of QFP edema (QFPE), mass effect and other patellofemoral joint pathologies. The cross-sectional area of QFP was measured and the amount of edema was recorded. RESULTS: QFPE was detected in 79 of the 340 patients with AKP (mean age: 32.29±8.81 years; range: 18–45 years). Mass effects were significantly more common in the AKP group (n=35, 44.3%, p=0.001). The risk of AKP in patients with mass effects was 38.973 times higher compared to patients without mass effects (p=0.001). Patients with diffuse QFPE had a higher risk of AKP than patients with less than 50% edema (p=0.021). Patients with patella alta and increased trochlear sulcus angle had a higher risk of AKP (p=0.029, p=0.006). No other variables were significant risk factors. There was no statistically significant cutoff value for the cross-sectional area. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: QFPE and mass effects may be associated with AKP independently of other patellofemoral joint pathologies. Therefore, radiologists should be aware of these common findings when analyzing MR images of patients with AKP. |
| 14. | Healthcare Shift Workers’ Sleep Quality, Daytime Sleepiness, and Circadian Preference Alperen Kılıç, Serhat Koran, Mehmet Yücel Ağargün doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.35744 Pages 156 - 164 INTRODUCTION: It was aimed to evaluate sleep quality, daytime sleepiness, and circadian rhythm types in healthcare workers working in shifts at different periods. METHODS: This cross-sectional study was conducted on 125 healthcare workers in a tertiary hospital between November and December 2018. Data were collected using Epworth Sleepiness Scale, Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire, and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Participants were divided into four groups: Those who do not work in shifts (Group 1), those who work in shifts between 18: 00 and 24: 00 (Group 2), those who work in shifts between 18: 00 and 08: 00 (Group 3), and all shift workers (Group 4). RESULTS: When Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores were compared, it was found that Group 4 (p=0.015) and Group 2 (p=0.007) were significantly more sleepy than Group 1. When the Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire results were compared, no significant difference was found between the groups in terms of both morningness, eveningness, and intermediate chronotypes, and MEQ scores. According to the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index total score, Group 2 (p=0.005), Group 3 (p=0.003), and Group 4 (p=0.001) had significantly more impaired sleep quality than Group 1. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Among healthcare workers, shift work is associated with poor sleep quality and excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS). When we compare the shift groups, although no significant relationship was found, Group 2 had relatively low sleep quality and EDS compared to Group 3. Although the weekly working time (h/week) is significantly less, we think that the main factor is that the weekly working periods of the Group 2 are more frequent than the Group 3. |
| REVIEW | |
| 15. | A Comprehensive Review for Refreshing the Crush Syndrome Knowledge After the Devastating Earthquake in Türkiye Ramiz Yazici, Can İlçin, Talha Özsu, Türker Demirtakan, Utku Murat Kalafat, Serkan Doğan doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.03511 Pages 165 - 170 On February 6, 2023, the southeastern region of Türkiye suffered from two consecutive devastating earthquakes with 7.6 and 7.8 magnificence. Since then, at least 44,324 deaths and approximately 200,000 wounded survivors have been reported. Clear evidences of mortality reasons have not been revealed; yet, we explicitly know from Marmara Earthquake in 1999 that many survivors died due to crush syndrome and associated complications. Crush syndrome is a systemic response of severe crush injury with hyperkalemia, acute kidney injury, and deep tissue damage. In crush syndrome, muscle damage initially occurs with the direct effect of trauma (baromyopathy), and later on, it develops with increased intramuscular pressure. Clinical findings consist of local inflammation findings in the traumatized area and systemic findings due to substances released from crushed muscle tissue into the systemic circulation. Earthquakes and other mass accident events leading to Crush Syndrome can place severe demands on local health-care systems. Excessive demand for dialysis machines, ventilators, and intensive care units can be necessary. |
| 16. | Usage of Fibrinogen Concentrate in Postpartum Hemorrhage: Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Perspective Ayça Sultan Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2023.02419 Pages 171 - 174 Postpartum hemorrhage is the most important cause of maternal death in the world. One of the best agents used to prevent massive bleeding is fibrinogen concentrate (FC). FC can control bleeding without causing viral complications and without volume overload as in transfusion-associated circulatory overload and transfusion-related acute lung injury. FC is easy to apply, does not require dissolution, no extra apparatus is needed. Considering blood and blood products used in large amounts, it is a cost-effective agent. |
| LETTER TO THE EDITOR | |
| 17. | Modified Thoracalumbar Interfascial Plane Block in Inguinal Hernia Repairment Engin İhsan Turan, Ayça Sultan Şahin doi: 10.14744/cm.2022.49358 Pages 175 - 176 Abstract | |